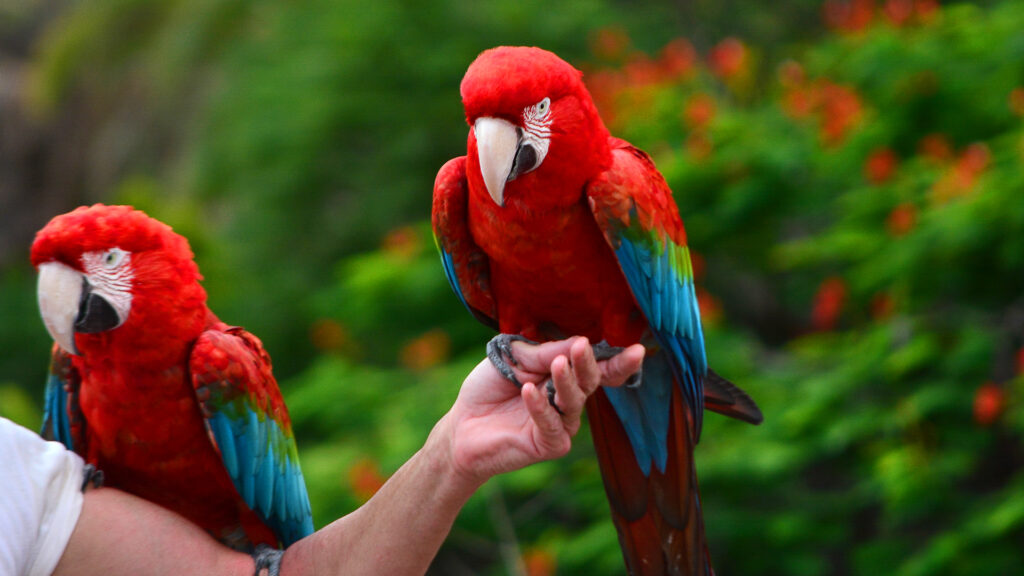
MACAW
Genera Ara, Anodorhynchus, and Primolius

Length
60 – 130 cm
weight

0,20 – 1,8 kg
Lifespan

60 años
Macaws are large, colorful, long-tailed Neotropical parrots belonging to the Psittacidae family. They inhabit diverse ecosystems in Central and South America and are famous for their intelligence, powerful vocalizations, and long-lasting pair bonds. The group ranges from agile and relatively small “mini-macaws” to the largest macaws in the world
.
General characteristics
Macaws have a strong, curved beak that they use not only to open seeds but also to climb and manipulate objects with great skill. Their feet have two toes pointing forward and two pointing backward, giving them excellent grip on branches and uneven surfaces. Their plumage is very varied and vibrant: it can be a mix of red, green, blue, and yellow tones, and some members of the group have featherless patches on their faces or small facial markings that each individual displays differently. Within the group, there are small, lightweight birds, but also some that are quite large, reaching almost a meter in length. Males and females often look so similar that they are difficult to distinguish at first glance.
Feeding
The diet of macaws consists mainly of fruits, seeds, and nuts, although they occasionally eat flowers and tender shoots. Certain species specialize in particularly hard seeds or palm fruits, which requires a very powerful beak; others, when resources are scarce, will even feed on nearby crops. Several members of the group visit clay licks along riverbanks, as this clay helps neutralize toxins present in some of the seeds they consume.
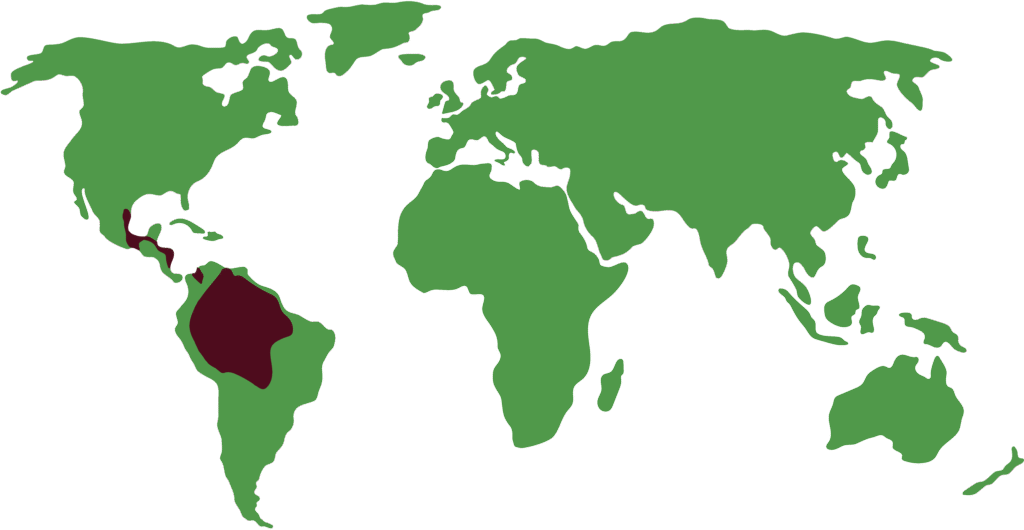
Distribution
Macaws occupy a wide range of habitats in Central and South America: humid and riparian forests, mature forests, wooded savannas, palm swamps, floodplains, and also semi-arid areas and rocky ravines in certain cases. Several species are generalists and tolerate disturbed landscapes; others depend strictly on mature forests or very specific formations (for example, palm groves) and, therefore, have very restricted ranges.
.
Behaviour
The social life of macaws can vary greatly: some species live primarily in pairs or small family groups, while others form large, highly active flocks. They are noisy birds and use loud calls to maintain contact between group members, even over long distances. Pairs often stay together for many years, working together to defend the nest and care for their young. In many cases, macaws forage in groups and fly in conspicuous and striking formations.
Reproduction
Macaws typically nest in hollows of large trees, although other members of the group also use cavities in cliffs or palm trees. They usually lay between one and three eggs, typically two or three. Incubation lasts around three to four weeks, and both parents closely assist in caring for the chicks. The chicks remain with the adults for several months, and in larger species, this period of dependence can be even longer.
Did you know?
The beak of a macaw is strong enough to crack extremely hard nuts; it also helps them climb.
Several species have given their names to flagship conservation projects due to their high risk status in the wild (e.g., the blue-throated macaw and the red-fronted macaw).
Macaws are monogamous for life: once they choose a mate, they stay together forever. They help each other preen, search for food, and care for their young.
Threats
The greatest threats to macaws come from deforestation, habitat fragmentation caused by agriculture and livestock farming, and the logging of trees they often use for nesting. They also suffer from illegal capture for the pet trade and, in some areas, competition with other species for nesting cavities. While some species are not at serious risk, others, with very small populations or very limited ranges, face a real danger of extinction. To help them, forest protection programs, captive breeding programs, controlled releases, and educational initiatives with local communities are being carried out. Thanks to these initiatives, several members of the group have become symbols of conservation and clear examples of why it is important to protect their habitats.
Conservation status