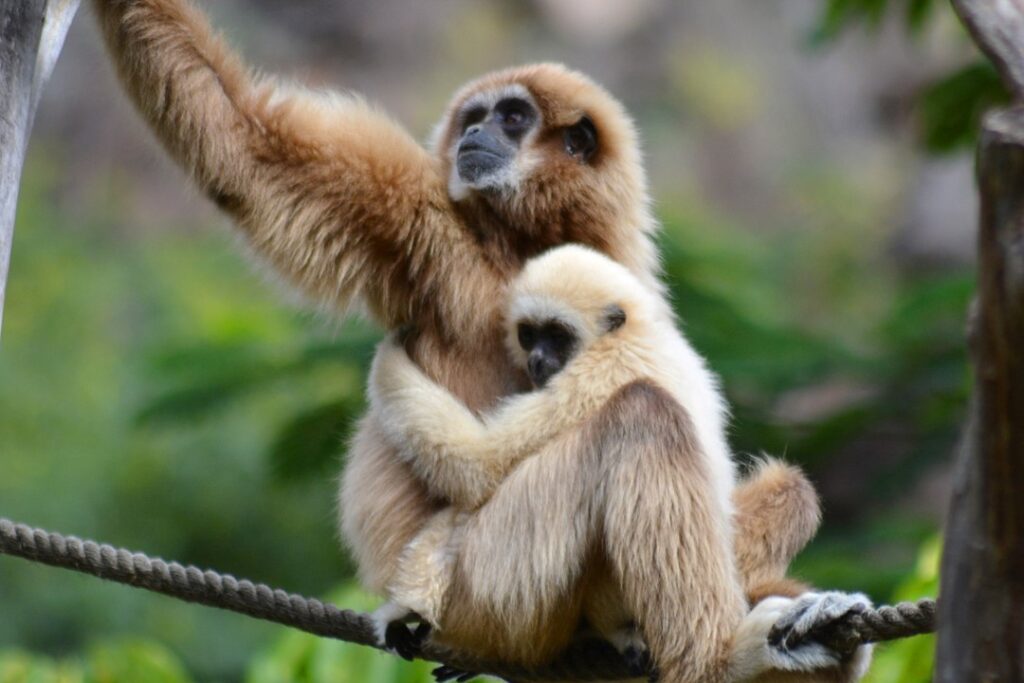
LAR GIBBON
Hylobates lar

Length
60 cm
weight

6 kg
Lifespan

30 years
The lar gibbon, also known as the white-handed gibbon, is one of the most agile and fast members of the primate order. They are great acrobats with formidable eyesight and extraordinary reflexes.
General characteristics
It´s hard to differentiate both genders at simple sight. Its height ranges from 40-60cm and it can reaches a maximum weight of 6kg. Its body is slender with very long arms and legs and has no tail. The arms are approximately 40% longer than the legs.
The color of its fur can be either black/dark brown or blond /eddish brown, but the hands and feet are always white, hence its name. Its face is black with a ring of white fur surrounding it.
Feeding
They feed primarily on fruit but also on leaves, insects and flowers.
Behaviour
They are tree-dwellers and use the brachiation method: they hang from trees, swinging like pendulums aided by their long arms and long fingers used as hooks. They rarely set their feet on the ground, where they move on their back legs.
Gibbon´s sound production is one of Palmito´s most characteristic sounds. They produce these sounds shortly after dawn to the point of engaging in real duet perfomances. The instigator is usually the female gibbon. In the wild, the purpose of these calls is to mark and delimit the boundaries of their territory, as they are very territorial animals. But the call is also used to reinforce the bond with partners or to warn others against looming dangers.
They live in families of 5 or 6 individuals on average, including the adult pair and offsprings of different ages, who are expelled from the group when they reach adulthood.
Reproduction
There is no specific breeding season for gibbons. Gestation lasts approximately 8 months, during which a calf is born and nursed for a year and a half. The mother is the main caregiver of the calf. The newborn clings to the hair of the female, who carries it in her arms as she moves from tree to tree.
Threats
It is an endangered species. The population has declined drastically due to the destruction of its habitat and the capture of gibbons for commercial purposes and for human consumption.
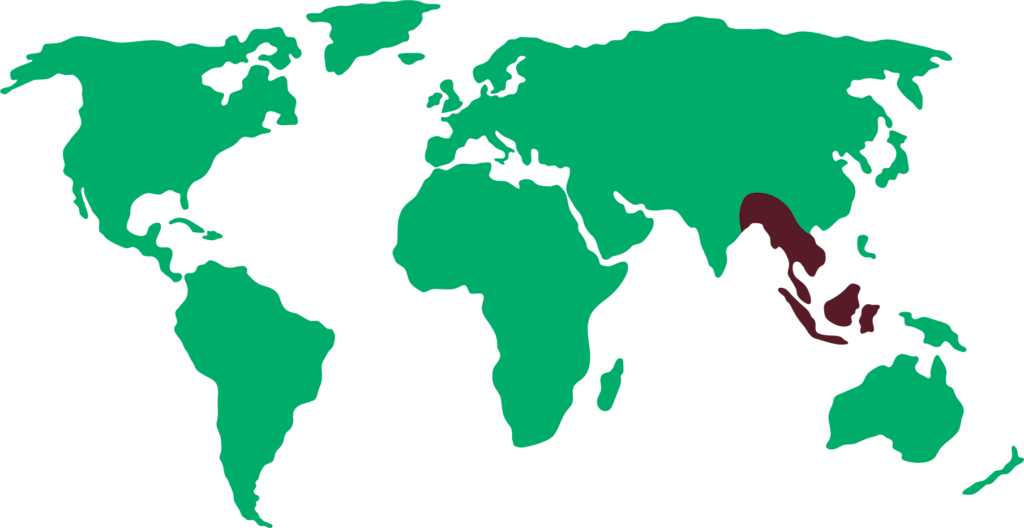
Distribution
They can be found in the humid forests of Southeast Asia, extending into Malaysia, Sumatra, Java and Borneo.
Did you know?
Gibbons are fitted with patches of hard skin designed for sitting, called ischial callosities.
When they are walking on the ground, they raise their arms to keep their balance.
They have a great affection to each other and frecuently express it through hugs and a facial expression that resembles the human smile.
Conservation status