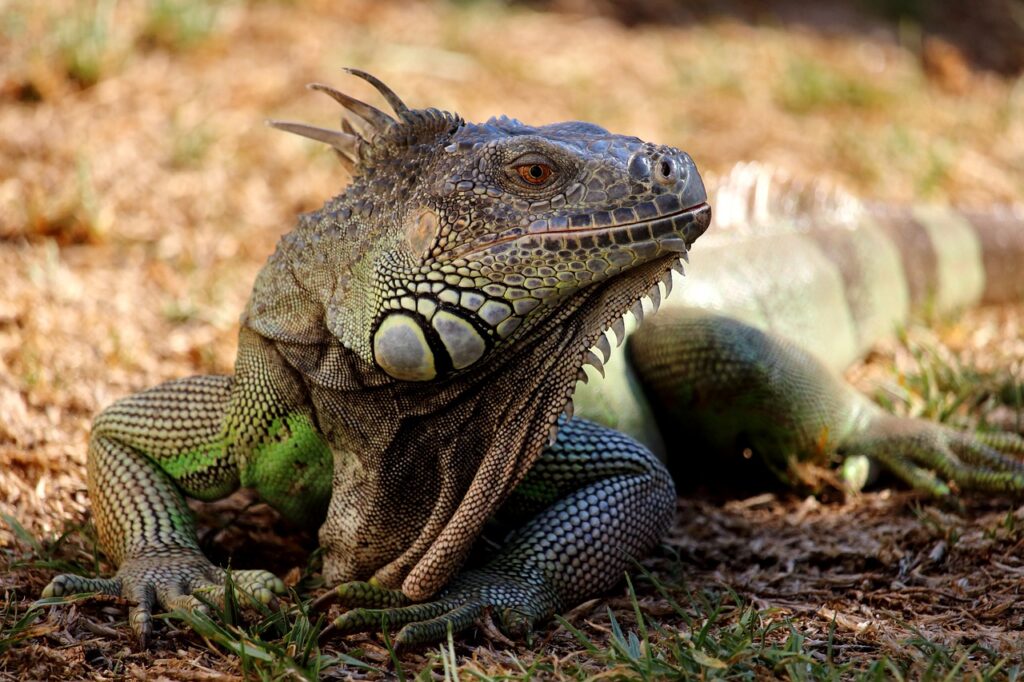
GREEN IGUANA
Iguana iguana

LENGTH
2 m
WEIGHT

15 kg
LIFESPAN

15 years
The green iguana, also known as the common iguana, is an arboreal lizard. Although they can measure up to 2 metres in total to the tip of the tail, if we only count the body to the cloaca, males can measure up to 40cm, while females are about 10cm shorter.
General characteristics
Their green colour allows them to camouflage themselves among the vegetation of the area. Their skin is made up of small scales that cover their entire body. They have a crest that runs from their head to their tail, which is larger in males than in females.
In addition, they also have a dewlap on their chin, which they use as a weapon of defence and for courting females.
Feeding
Iguanas are herbivorous animals. They usually feed on flowers, fruits and leaves.
Behaviour
Like all reptiles, green iguanas are cold-blooded animals, so as soon as the sun starts to shine, they climb up to the highest branches of trees in order to get the perfect temperature they need.
Iguanas are solitary animals and only gather with other individuals during the breeding season. Groups of 5 to 8 individuals are formed, usually consisting of a male, females and some juveniles.
There´s daily routine that they follow to the letter. They are diurnal animals, so when the sun rises they wake up and go to a place where the sun is shining in order to gather energy that they will then use to forage for food. Around midday, they go in search of food, and once they have finished, they return to the sun to continue resting. When the sun begins to set, they look for a place where they can take shelter from predators at night and rest.
Reproduction
They are oviparous, which means that they lay eggs. Once the mating season starts, iguanas only focus on mating. Females usually choose the larger or more dominant male. Iguana gestation lasts about two months, and to lay their eggs they dig tunnels where they leave the eggs until they hatch after about 80 days.
Threats
The hunting of these animals for fur, the sale of exotic animals or even as food in some countries has resulted in this species being listed in CITES Appendix II, which means that its trade must be limited and controlled, otherwise it could eventually become an endangered species.
Other threats are animals such as badgers, dogs and cats, or raccoons that destroy the nests to eat the eggs.
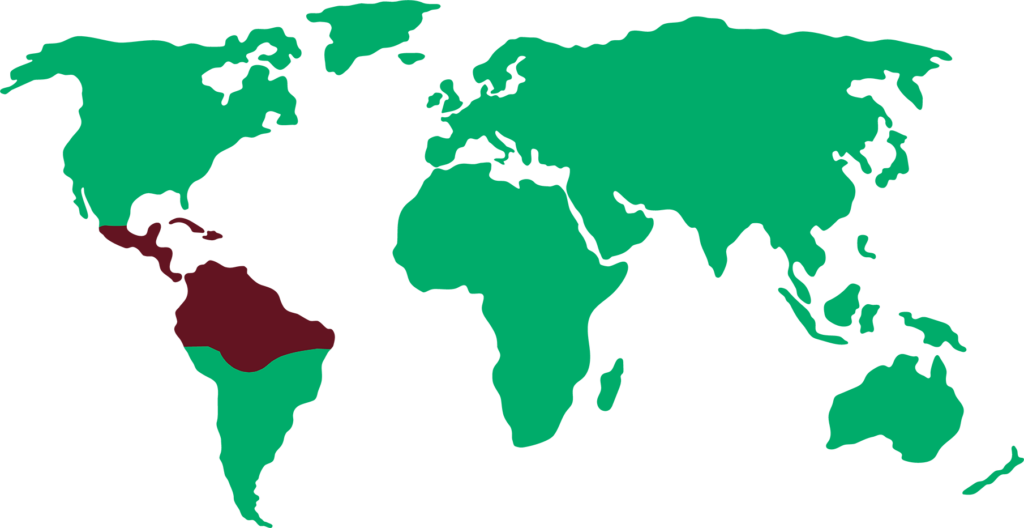
Distribution
Green iguanas can be found from Mexico to Brazil and Paraguay. They can also be found in the Caribbean and Florida. Iguanas like areas with a lot of vegetation and at high altitudes, such as mangroves, jungles, grasslands, etc. They look for warm areas around 28ºC and around 70% humidity. It is important that they have areas with trees as they spend most of their time there.
Did you know?
They like to be in trees near water so that they can dive into the water if they are in danger.
They can be submerged in water for up to 15 minutes.
The green iguana is the most widely traded exotic pet.
Conservation status